Bike Calorie and Hydration Calculator
Welcome to our Bike Calorie and Hydration Calculator! This handy tool will help you estimate the number of calories burned and fluid intake required for your next ride. Designed with your personal factors in mind, such as age, gender, riding time, and intensity, this calculator aims to provide you with a tailored overview of your nutritional and hydration needs.
Cycling Calorie and Hydration Calculator
Calories needed:
Fluid needed (liters):
User Guide: Using the calculator is simple:
- Enter your age in years.
- Select your gender from the dropdown menu.
- Choose the intensity of your ride: slow, medium, or fast.
- Input the duration of your ride in hours.
- Click the “Calculate” button.
The calculator will instantly display the estimated number of calories burned during your ride and the amount of fluid intake required in liters. Use this information to plan your nutrition and hydration strategy for a successful and enjoyable cycling experience.
Disclaimer: Please note that the results provided by this calculator are estimates and should not be considered as professional advice. Individual calorie expenditure and hydration requirements may vary based on factors such as body composition, metabolism, and environmental conditions. It’s always a good idea to consult with a sports nutritionist for personalized recommendations. Remember to listen to your body and adjust your nutrition and hydration plans accordingly. Stay safe and enjoy your ride!
How the Cycling Calorie and Hydration Calculator Works
Before diving into the details of cycling nutrition and hydration, let’s discuss how our calculator works. The calculator takes into account four essential factors:
- Age
- Gender
- Riding intensity (slow, medium, or fast)
- Riding duration (in hours)
By considering these factors, the calculator estimates the number of calories burned during the cycling session and the amount of fluid intake required to stay adequately hydrated.
The cycling calorie and hydration calculator uses the following equations:
- Calorie Consumption:
Calories Burned = MET × Weight (kg) × Duration (hours)
MET values for different cycling intensities are sourced from the Compendium of Physical Activities. You can find more information on MET values here: https://sites.google.com/site/compendiumofphysicalactivities/
- Fluid Intake:
- For rides shorter than an hour: aim for 150-250ml of fluid every 15-20 minutes.
- For rides longer than an hour: aim for 400-800ml of fluid per hour.
These fluid intake guidelines are based on recommendations from sports nutrition experts and organizations such as the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). You can find more information on ACSM’s hydration guidelines here: https://www.acsm.org/docs/default-source/files-for-resource-library/hydration_tip_sheet.pdf
You may find helpful: Cycling for Beginners: 30 Essential Tips for New Riders
The Importance of Nutrition and Hydration in Cycling

Calorie Consumption and Energy Expenditure
Cycling is a physically demanding activity that requires a significant amount of energy. The energy expended during cycling is measured in calories, which are units of energy. The number of calories burned during a cycling session depends on factors such as age, gender, body weight, and exercise intensity.
Age and Gender
As we age, our metabolic rate tends to slow down, which means we burn fewer calories during physical activities. Additionally, men generally have a higher basal metabolic rate (BMR) than women due to their greater muscle mass. This results in a higher calorie expenditure for men compared to women of the same age, weight, and exercise intensity.
Riding Intensity
The intensity of your cycling session plays a significant role in determining the number of calories burned. Higher-intensity workouts, such as fast-paced cycling, will burn more calories than lower-intensity workouts, such as leisurely rides.
Fluid Intake and Hydration
Staying hydrated during a cycling session is crucial for optimal performance and preventing dehydration. When you exercise, your body loses fluids through sweat, which can lead to dehydration if not replaced. Dehydration can negatively affect your physical and mental performance, increasing the risk of cramps, dizziness, and fatigue.
The amount of fluid intake required during a cycling session depends on factors such as age, gender, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions.
Factors Affecting Fluid Loss and Intake Recommendations
Exercise Intensity
Higher-intensity cycling sessions lead to increased sweat production and, consequently, greater fluid loss. To maintain optimal hydration levels, it’s essential to consume more fluids during high-intensity rides.
Environmental Conditions
Temperature and humidity are two critical environmental factors that affect fluid loss during cycling. High temperatures and humidity can increase sweat production, leading to greater fluid loss and a higher risk of dehydration.
Individual Variability
Fluid loss and intake requirements can vary greatly between individuals due to factors such as body composition, sweat rate, and acclimatization to heat. It’s essential to monitor your fluid loss during exercise and adjust your intake accordingly.
Calorie and Fluid Intake Guidelines for Cyclists

Pre-ride Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration before a cycling session are crucial for ensuring adequate energy levels and preventing dehydration.
Calorie Intake
Consume a well-balanced meal 2-3 hours before your ride, focusing on carbohydrates, moderate protein, and low fat. This will provide you with the necessary energy to fuel your cycling session. Some examples of pre-ride meals include:
- Whole-grain pasta with tomato sauce and lean protein
- Brown rice with vegetables and grilled chicken
- A smoothie made with fruit, yogurt, and a scoop of protein powder
Hydration
Begin hydrating 2-3 hours before your ride by consuming 500-600ml of water or an electrolyte drink. This will help to ensure that you start your cycling session adequately hydrated.
During-ride Nutrition and Hydration
Calorie Intake
For rides lasting longer than 90 minutes, it’s essential to consume additional calories during the ride to maintain energy levels. Aim to consume 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour, which can be obtained from various sources, such as energy bars, gels, or sports drinks. It’s important to experiment with different types and brands of nutrition products to find what works best for you. Some examples of during-ride nutrition include:
- Energy bars made with whole grains and natural sugars
- Energy gels that provide quick-absorbing carbohydrates
- Sports drinks containing carbohydrates and electrolytes
Hydration
Staying hydrated during your ride is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Aim to consume 150-250ml of fluid every 15-20 minutes, adjusting your intake based on factors such as exercise intensity, environmental conditions, and individual sweat rate. Choose a combination of water and electrolyte drinks to replace both fluids and essential minerals lost through sweat.
Post-ride Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration after your ride are essential for promoting recovery and replenishing energy stores.
Calorie Intake
Consume a balanced meal within 30-60 minutes after your ride, focusing on carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and protein to support muscle repair. Some examples of post-ride meals include:
- Whole-grain sandwich with lean protein, vegetables, and avocado
- Quinoa salad with grilled vegetables and tofu or chicken
- Greek yogurt parfait with fruit and granola
Hydration
Continue to hydrate after your ride by consuming water or electrolyte drinks. Aim to replace 125-150% of the fluid lost during the ride within 2-4 hours post-exercise. This can be estimated by monitoring your weight before and after the ride, with each kilogram of weight loss representing approximately 1 liter of fluid loss.
Monitoring Your Nutrition and Hydration Status
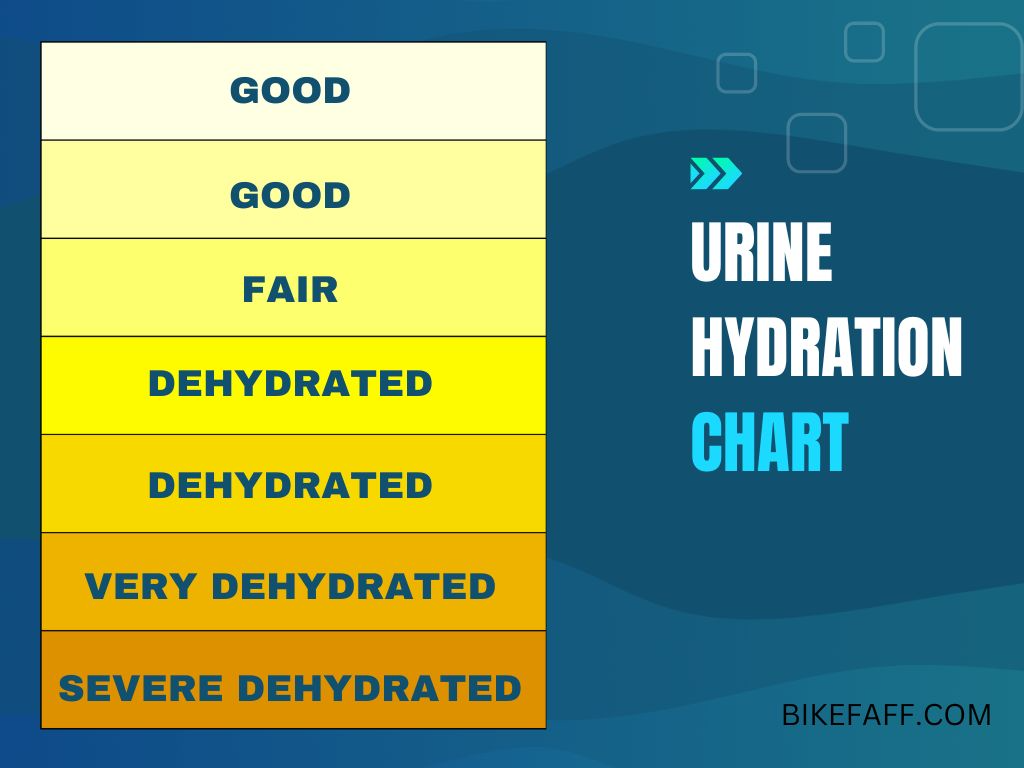
Body Weight and Urine Color
Monitoring your body weight and urine color can provide valuable information about your hydration status. A consistent decrease in body weight over several days may indicate inadequate fluid intake, while dark-colored urine can be a sign of dehydration. Aim to maintain a stable body weight and produce light-colored urine to ensure proper hydration.
Adjusting Calorie and Fluid Intake Based on Individual Needs
It’s important to remember that the calculator provides general guidelines for calorie and fluid intake during cycling. Individual needs can vary significantly based on factors such as body composition, fitness level, and training goals. Monitor your performance, energy levels, and recovery, and adjust your calorie and fluid intake as needed to optimize your cycling experience.
You may also like: